Principle of virtual work examples
What is the principle of virtual work? How are virtual methods work? Generalized Coordinates 2. Identify forces that do work 3. Analyze motion of points at which forces act 4. A virtual force is any system of forces in equilibrium.
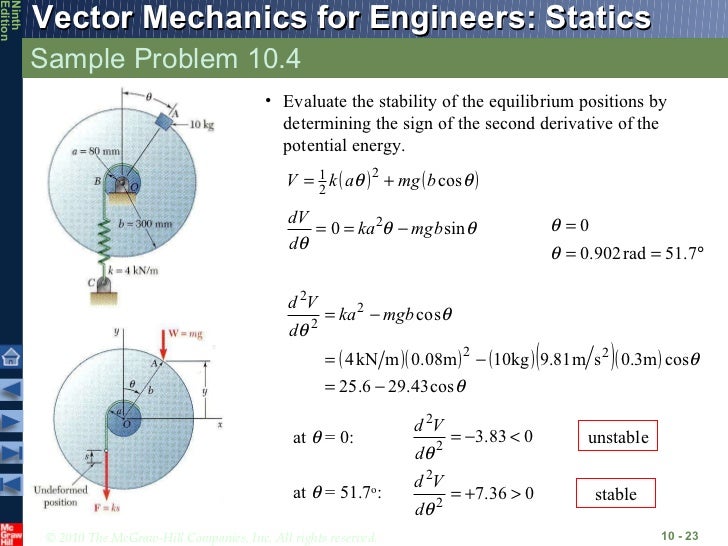
Weight of the body is negligible. Rotating the threaded rod AC of the automobile jack causes joints A and C to move closer together, thus raising the weight W. Determine the axial force in the ro if = 30° and W = kN. Chapter principle of virtual work 1. Virtual Work Examplepage of 5. Mechanical Efficiency Sample Problem 10. This is the principle of virtual work.
Assuming that Young’s modulus, the length, and the moment of inertia for the beam are, , and, respectively, verify that the principle of virtual work applies when a virtual parabolic displacement is applied to the beam. Likewise in solving a problem by the principle of virtual work, it is always essential to say whether you are describing the work done by a force on what part of the system (on the ladder or on the floor?) and whether you are describing an increase or a decrease of some length or angle.
That is, the principle of virtual work can be derived from these conditions, and conversely. Here is a typical example of how we can apply the principle of virtual work to find the deflections at some point in an elastic solid. Example principle of virtual work From the principle of virtual work, −δWi−δWe= Wδz−PδV = 0. Geometrically admissible virtual displacements δV and δz are related according to δV = 4δz. In a 1D problem, nodes are surfaces.
There is also a corresponding principle for static systems called the principle of virtual work for applied forces. Example: Find B, the vertical displacement at B. Principle of virtual work.
A very similar method is to use the principle of virtual work. In this metho we imagine that we act upon the system in such a manner as to increase one of the coordinates. We imagine, for example, what would happen if we were to stretch one of the springs, or to increase the angle between two jointed rods, or the angle that the ladder makes as it leans against the wall. Neglect the weight of the bell crank.
W Wspr Wapl kx Fapl x(.1) There are two ways of viewing this expression. First, if the system is in equilibrium (kx Fapl ) then the virtual work is zero, W 0. Alternatively, if the virtual work is zero then, since xis arbitrary, the system must be in equilibrium. Feynman is using definite small quantities (inches) in place of infinitessimals etc.

Probably he wanted to avoid non-essential mathematical formality, in line with his casual, hand-waving persona. Need to repeat analysis for different points. Can be used to calculate displacements at some key points. The total virtual work is.
Note that the principle of virtual work in the form 3. This concept of minimum total potential energy is nothing but can be called as the special case of the virtual work principle. Application of Minimum Potential Energy in case of a beam and truss is also explained.
All bars are of equal length L and same EA. Assume there is no change in temperature from the stress free state. In this example, we used a simple truss to illustrate the principle of virtual work.
However, its application encompasses beams, frames and even complex trusses with numerous members. Calculation by hand will no doubt be tedious however, a computer program can be written for the entire structure and then subsequently used to compute the displacements at the desired points.
Truss members AD and DE increase in temperature 40℃. Member CE decreases in temperature 30℃.
If a rigid body is in equilibrium, the total virtual work of external forces acting on the body is zero for any virtual displacement of the body.
Yorumlar
Yorum Gönder